During the period, 600,000 feet of flat nylon cord costing $330,000 were purchased and used. When a company makes a product and compares the actual materials cost to the standard materials cost, the result is the total direct materials cost variance. When a company makes a product and compares the actual materials cost to the standard materials cost, the result is the total direct materials cost variance.

Sweet and Fresh Shampoo Overhead
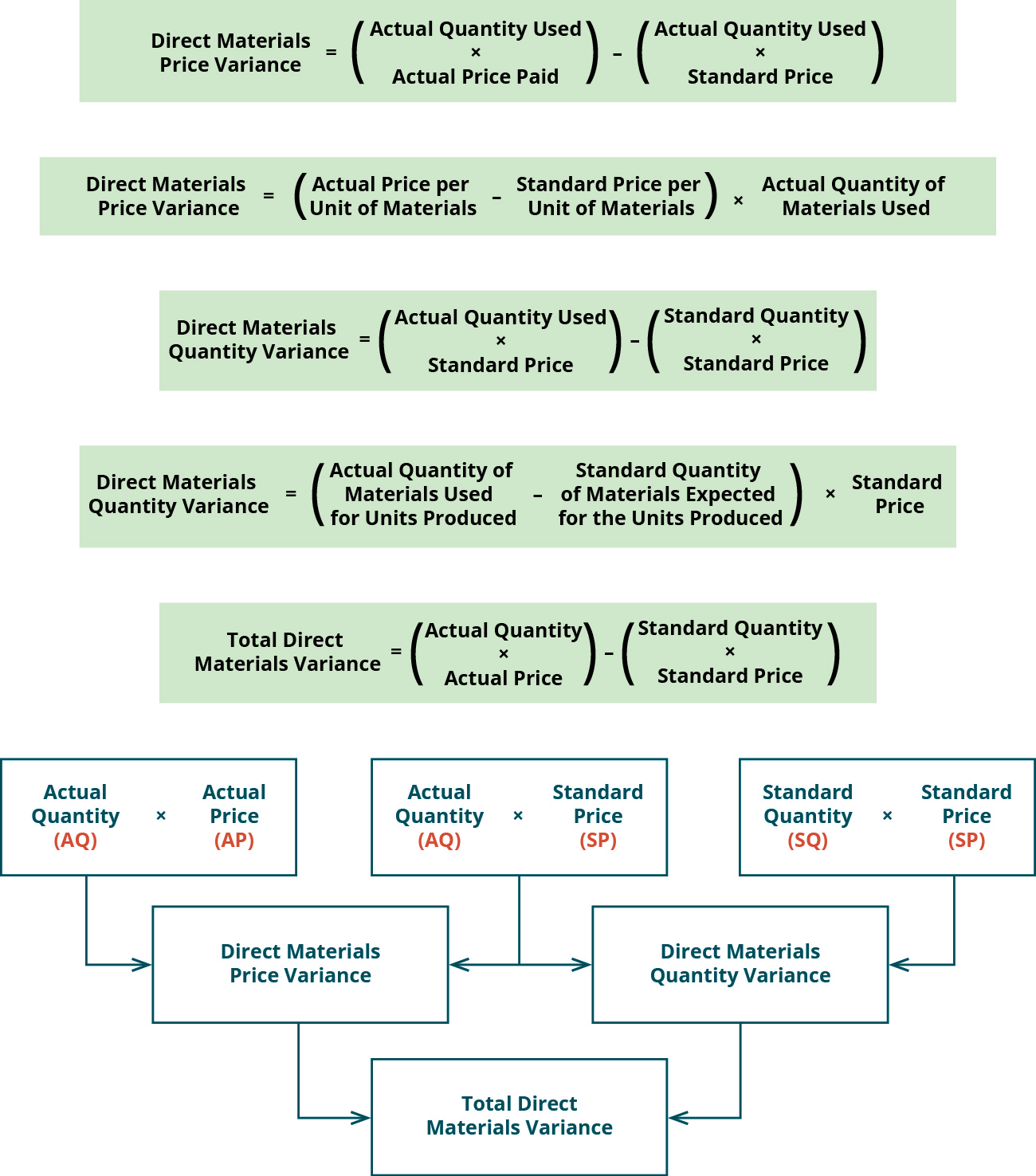
The total direct labor variance is the total standard labor costs allowed of $675,000 less the actual amount paid for direct labor of $832,500, which is $(157,500) unfavorable. Total standard quantity is calculated as standard quantity per unit times actual production or 0.25 direct labor hours per unit times 150,000 units produced equals 37,500 direct labor hours. Total direct labor costs per the standard amounts allowed are calculated as total standard quantity (37,500) times standard rate per hour ($18) equals $675,000. During the period, Brad projected he should pay $675,000 for direct labor to produce 150,000 units. Refer to the total direct materials variance in the top section of the template. Total standard quantity is calculated as standard quantity per unit times actual production or 4.2 feet of flat nylon cord per unit times 150,000 units produced equals 630,000 feet of flat nylon cord.
Direct materials price variance
This overage in direct labor hours means that $22,500 of additional variable manufacturing overhead was incurred based on the standard amount applied per direct labor hour. Inefficient use of the cost driver used to apply variable manufacturing overhead typically results in additional overhead costs. A template to compute the total variable manufacturing overhead variance, variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance, and variable manufacturing overhead rate variance is provided 3 ways to build assets in Exhibit 8-9. A template to compute the total direct labor variance, direct labor efficiency variance, and direct labor rate variance is provided in Exhibit 8-6. Figure 8.5 shows the connection between the variable overhead rate variance and variable overhead efficiency variance to total variable overhead cost variance. In this case, the actual price per unit of materials is $6.00, the standard price per unit of materials is $7.00, and the actual quantity used is 0.25 pounds.
© Accounting Professor 2023. All rights reserved
During the period, 45,000 direct labor hours were worked and $832,500 was paid for direct labor wages. The total direct materials variance is calculated as the total standard costs allowed for direct materials of $315,000 less the actual amount paid of $330,000 equal the total direct materials variance of $(15,000) U. The direct materials price variance of Hampton Appliance Company is unfavorable for the month of January. This is because the actual price paid to buy 5,000 units of direct material exceeds the standard price. In this case, the actual price per unit of materials is $9.00, the standard price per unit of materials is $7.00, and the actual quantity used is 0.25 pounds. The direct materials variances measure how efficient the company is at using materials as well as how effective it is at using materials.
An investigation may reveal that employees took longer than 0.25 hours to make each unit, which could mean additional training or another appropriate solution. Using the standard and actual data given for Lastlock and the direct materials variance template, compute the direct materials variances. In conclusion, efficiency variance is a crucial metric for any manufacturing company looking to increase profitability and reduce waste. By understanding and monitoring efficiency variance, companies can identify areas where they can improve their processes, reduce costs, and increase productivity.
- Let’s assume that the Direct Materials Usage Variance account has a debit balance of $2,000 at the end of the accounting year.
- Each output unit should be paid based on the total material costs or wages during the measuring period.
- Knowledge of this variance may prompt a company’s management team to increase product prices, use substitute materials, or find other offsetting sources of cost reduction.
- It’s thus typical for management personnel to set expectations and benchmarks for both costs and output, while the manufacturing activity is still in its planning stage before the production process even starts.
- Standard variances are considered a red flag for management to investigate and determine their cause.
- Although the new fabricator was less experienced, her pay rate per hour was lower.
Efficiency variance can have a significant impact on the company’s profitability. Ignoring efficiency variance can lead to continued inefficiencies, resulting in decreased profitability for the company. Efficiency variance can be an indicator of decreased productivity, which can lead to delays in production and missed deadlines. If efficiency variance is ignored, these issues can continue to decrease overall productivity. New equipment may incorporate technological advances that can improve efficiency and reduce variance.
If a company lacks the necessary expertise or resources to efficiently perform a specific process, outsourcing can be a good solution. For example, suppose a company lacks the technology required or skilled labor to perform a particular process. In that case, outsourcing to a third-party provider can help them improve efficiency and reduce variance. Efficiency variance can lead to health and safety risks, such as equipment malfunctions and worker injuries.
The producer must be aware that the difference between what it expects to happen and what actually happens will affect all of the goods produced using these particular materials. Therefore, the sooner management is aware of a problem, the sooner they can fix it. For that reason, the material price variance is computed at the time of purchase and not when the material is used in production. The fixed component of manufacturing overhead is comprised of overhead costs that stay the same in total regardless of the quantity produced or another cost driver.