Net realizable value for inventory is the estimated selling price of inventory in the ordinary course of business, minus the estimated costs of completion and sale. For instance, if inventory sells for $500 and costs $100 to complete and sell, the NRV is $400, reflecting the inventory’s true market value. Net realizable value is an essential tool in accounting, ensuring that asset values are reported accurately and conservatively. By incorporating NRV, businesses can maintain compliance with accounting standards, make informed decisions, and provide stakeholders with a realistic view of their financial health. Despite its advantages, calculating NRV can be complex and time-consuming, requiring precise estimates and regular adjustments due to market fluctuations. Net realizable value ensures accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards by providing a conservative valuation of assets.
What are the requirements of IAS 2?
- The ultimate goal of NRV is to recognize how much proceeds from the sale of inventory or receipt of accounts receivable will actually be received.
- No one should act upon such information without appropriate professional advice after a thorough examination of the particular situation.
- Keep in mind that this should follow the conservatism principle in accounting.
- These examples show how NRV helps businesses determine the actual value they can expect from their assets, whether it’s inventory or accounts receivable.
- Consequently, officials for Dell Inc. analyzed the company’s accounts receivable as of January 30, 2009, and determined that $4.731 billion was the best guess as to the cash that would be collected.
Our AI-powered Anomaly Management Software helps accounting professionals identify and rectify potential ‘Errors and Omissions’ throughout the financial period so that teams can avoid the month-end rush. The AI algorithm continuously learns through a feedback loop which, in turn, reduces false anomalies. We empower accounting teams to work more efficiently, accurately, and collaboratively, enabling them to add greater value to their organizations’ accounting processes. It allows users to extract and ingest data automatically, and use formulas on the data to process and transform it. US GAAP does not permit a write-up of write-downs reported in a prior year, unlike international reporting standards, even if the net realizable value for inventory has been recovered.
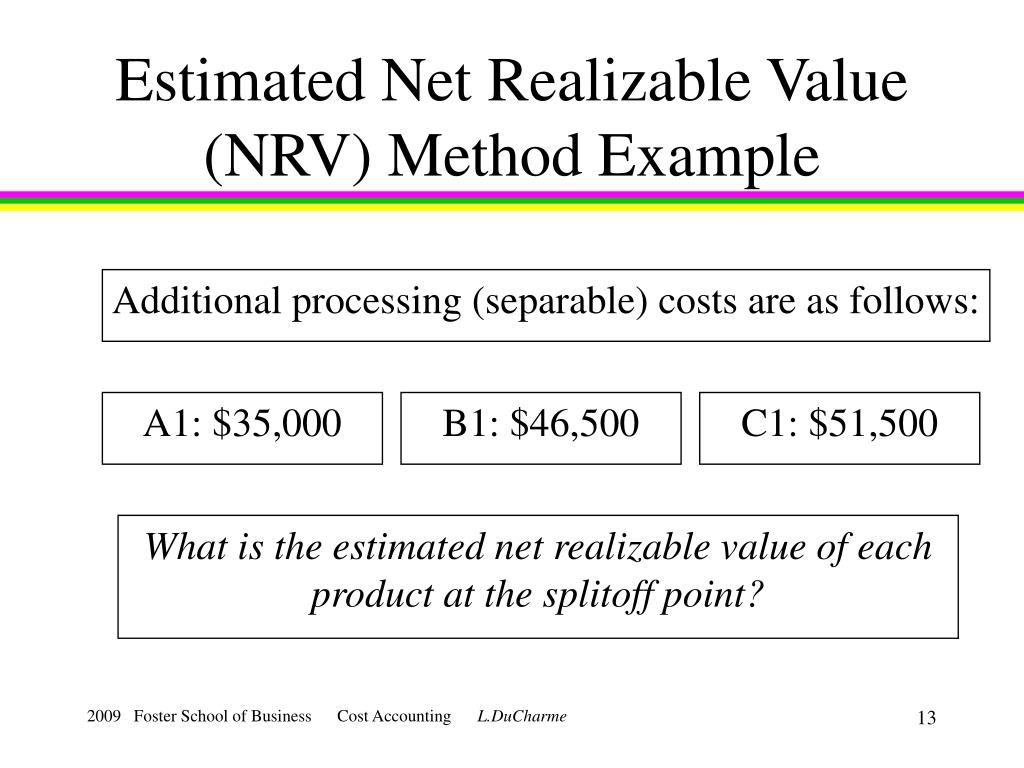
Net Realizable Value Formula
Companies that prioritize customers with higher credit strength will have higher NRV. The costs necessary to bring the inventory to its present location – e.g. transport costs incurred between manufacturing sites are capitalized. The accounting for the costs of transporting and distributing goods to customers depends on whether these activities represent a separate performance obligation from the sale of the goods. IAS 2 requires the same cost formula to be used for all inventories with a similar nature and use to the company, even if they are held by different legal entities in a group or in different countries. In practice, for an acquired business this often requires rapid realignment to its new parent’s group methodologies and systems.
Order to Cash
1As indicated previously, other versions of generally accepted accounting principles do exist. Equally as important, every party analyzing the resulting statements must possess the knowledge necessary to understand the multitude of reported figures what is a triple net nnn lease and whats included in it and explanations. If appropriate decisions are to result based on this information, both the preparer and the reader need an in-depth knowledge of U.S. Is it worth it to hold on to that equipment or would you be better off selling it?
Inventory Measured Using Any Method Other Than LIFO or the Retail Inventory Method
US GAAP, on the other hand, specifies the lower cost or market to value inventories. Market value, for this purpose, is defined as the current replacement cost subject to upper and lower limits. NRV helps business owners and accountants understand the true value of an asset. The conservative principles involved in the calculation prevent the overstatement of assets. It also allows for the conservative and appropriate recording of assets for a business.
Lower of cost or market (old rule)
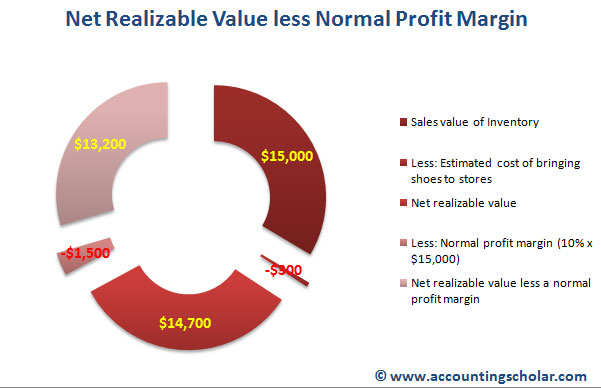
Except, when you were doing the LCM calculation, if that market price was higher than net realizable value (NRV), you had to use NRV. If the market price was lower than NRV minus a normal profit margin, you had to use NRV minus a normal profit margin. For instance, if the debit balances in the account receivables are $10,000 and have a credit balance of $800, then $9,200 is the resulting value of accounts receivables in the net realizable value method. Net realizable value of accounts receivable minus the credit balance give you the NRV, which can also be expressed as a debit balance in the asset account.
US GAAP does not provide specific guidance around accounting for assets that are rented out and then subsequently sold on a routine basis, and practice may vary. Proceeds from the sale would be accounted for in a manner consistent with the nature of the asset, which may be different from IFRS Standards. Because the estimated cost of ending inventory is based on current prices, this method approximates FIFO at LCM. By adjusting the inventory down, the balance sheet value of the asset, Merchandise Inventory, is restated at a more conservative number. Notice that we never adjust inventory up to fair market value, only downward.
This was updated in 2015 to where companies must now use the lower of cost or NRV method, which is more consistent with IFRS rules. In essence, the term “market” has been replaced with “net realizable value.” Companies must now use the lower cost or NRV method, which is more consistent with IFRS rules. NRV is important to companies because it provides a true valuation of assets. NRV is a conservative method for valuing assets because it estimates the true amount the seller would receive net of costs if the asset were to be sold.